Scrap tire shredding equipment line: igniting the engine of the circular economy
Once considered a troublesome source of “black pollution,” waste tires have now been transformed from waste into valuable resources with the help of waste tire shredding equipment lines. Investing in such equipment lines is of immeasurable value, not only for the development of the enterprise itself, but also for the sustainable development of the entire social economy and environment.
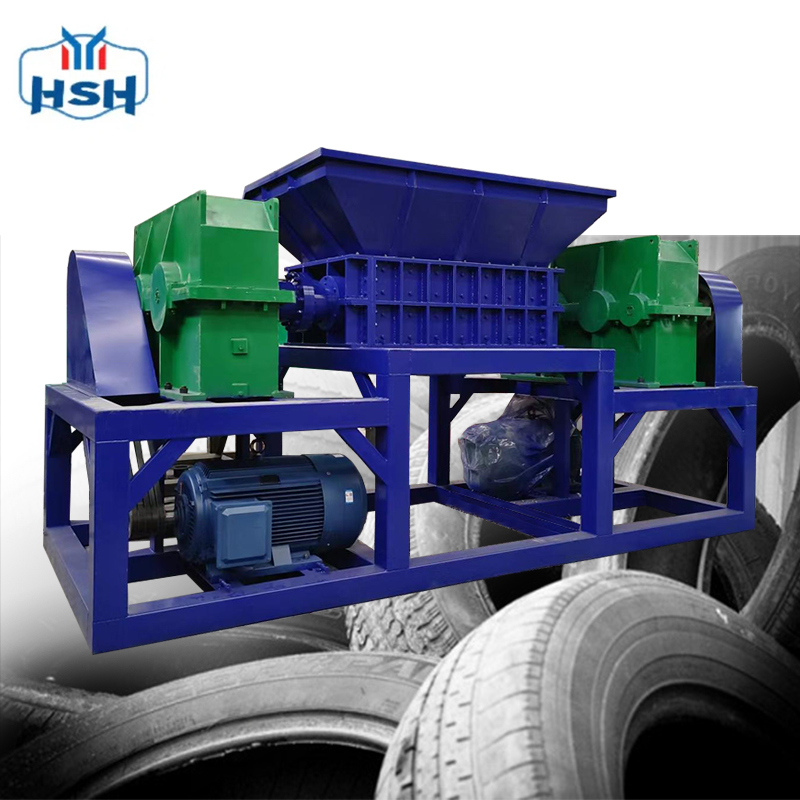

From an investment return perspective, the waste tire shredding equipment line demonstrates significant economic potential. For instance, the equipment line developed by RuiSaiKe Machinery Equipment Co., Ltd. employs physical mechanical methods to process waste tires through a series of precise processes, including fiber separation, shredding, steel wire separation, and rubber particle and rubber powder separation. According to actual operational data, investing in this production line yields a profit of approximately 3,000 yuan per ton of processed waste tires. This profit margin has attracted the attention of many investors, and the equipment line has been successfully applied in multiple cities across China. A small resource recycling company in Hebei Province initially invested in a production line with a processing capacity of 500 kilograms per hour. Under proper management, the company achieved profitability within just six months. As the business continues to expand, the company plans to add another production line with greater processing capacity within the next year to further scale up production and enhance economic benefits.
From a macro perspective on industrial development, waste tire shredding equipment lines have driven the upgrading of the entire waste tire recycling industry. In the past, the waste tire processing industry was relatively rudimentary, often relying on outdated methods such as crude oil refining, which not only caused environmental damage but also resulted in low resource utilization rates. Now, equipment lines are driving the industry toward more specialized and refined development. On one hand, the widespread adoption of equipment lines has stimulated the coordinated development of upstream and downstream related industries. Upstream equipment manufacturing companies have increased their R&D investments to enhance equipment performance and quality, driving technological innovation in the machinery manufacturing industry. Downstream companies producing rubber products and building materials using recycled rubber particles and rubber powder as raw materials have gained access to stable and high-quality raw material supplies, enabling them to develop new products, expand market share, and promote the prosperous development of the entire industrial chain. On the other hand, the widespread adoption of the equipment line within the industry has attracted more professional talent to the field of waste tire recycling and utilization, injecting new vitality into industrial development and promoting the optimization and upgrading of the industry's talent structure.
In terms of environmental protection and sustainable development, waste tire shredding equipment lines play an irreplaceable key role. Under the backdrop of the “dual carbon” goals, these equipment lines have made positive contributions to carbon emissions reduction. For example, waste tire shredding production lines utilize environmental protection technologies such as enclosed conveying and negative pressure dust suppression, not only effectively controlling the emission of pollutants like dust but also reducing the generation of greenhouse gases during the processing. For every certain amount of waste tires processed, compared to traditional processing methods, it significantly reduces the emission of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, supporting China's carbon reduction goals. Additionally, the equipment line converts waste tires into reusable resources, reducing the extraction and consumption of virgin resources, aligning with sustainable development principles. This leaves future generations with more valuable resource wealth and promotes the coordinated and sustainable development of the entire socio-economic and environmental sectors.