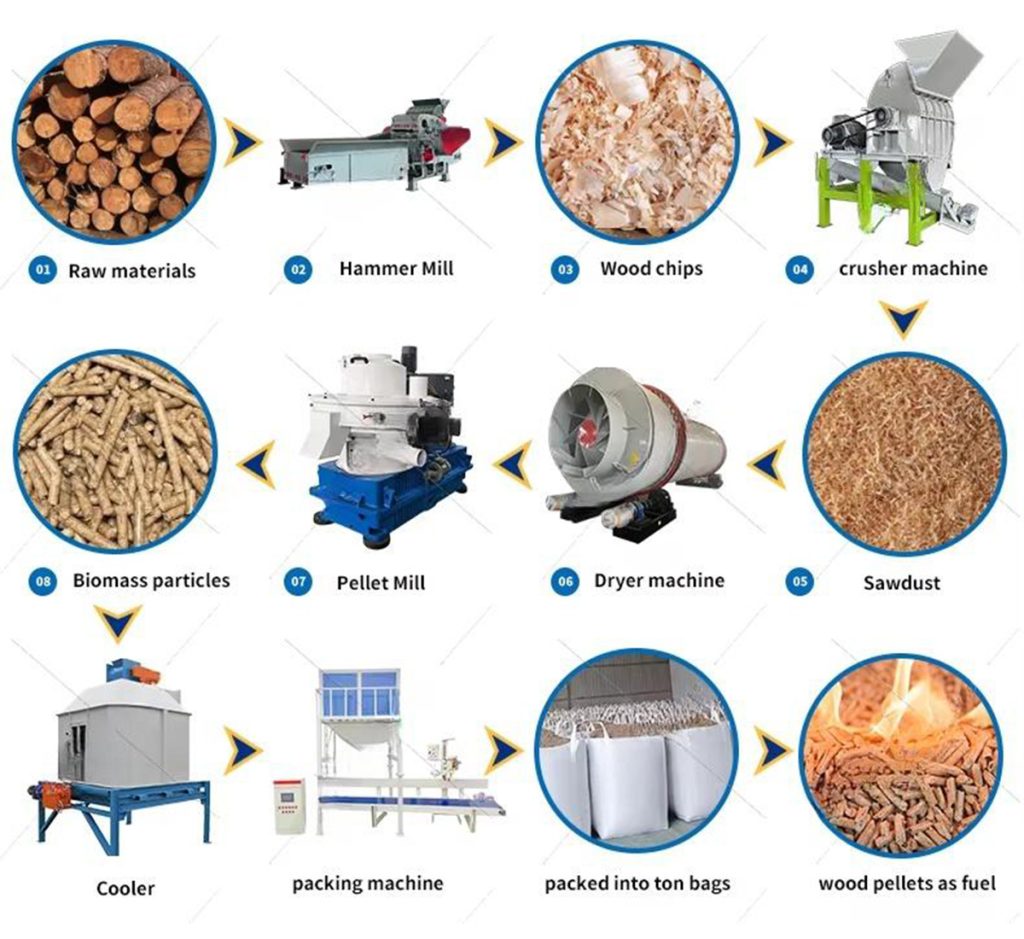
Global environmental policies are increasingly shaping the development trajectory of the shredder industry, driving technological innovation while expanding market demand across various regions. This interplay between regulation and industry response creates new opportunities for foreign trade enterprises.
The European Union’s Circular Economy Action Plan has become a key driver of shredder innovation. Stricter recycling targets for packaging waste (85% by 2030) have forced manufacturers to develop high-precision shredders with integrated sorting systems. These machines can separate different materials at a rate of 2-3 tons per hour, with AI-powered sensors identifying plastics, metals, and paper with 98% accuracy. Such advancements have boosted shredder imports in Germany and the Netherlands by 18% annually, as recycling facilities race to meet EU standards.

In North America, the U.S. EPA’s Waste Reduction Act and Canada’s Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) laws have focused on e-waste and electronic device recycling. This has spurred demand for specialized shredders equipped with anti-static components and dust collection systems to safely process circuit boards and batteries. Sales of these models have grown 22% year-over-year, with California and Ontario emerging as major markets due to their stricter local regulations.
Asian markets are also responding to tightening environmental policies. China’s "Dual Carbon" goals have led to a 30% increase in shredder adoption in waste-to-energy plants, particularly models designed for municipal solid waste (MSW) processing. These shredders feature high-torque motors and wear-resistant blades to handle 10-15 tons of MSW daily, supporting the country’s shift from landfills to incineration with energy recovery. Similarly, Japan’s Plastic Resource Circulation Act has driven demand for compact shredders in retail and food industries, with monthly sales exceeding 2,000 units in 2024.
Technical adaptations to meet these policies include modular designs that allow easy upgrades to comply with evolving regulations. For example, shredders now feature interchangeable blades for different material types and software updates to adjust processing parameters based on new waste classification standards. These flexible systems command 15-20% price premiums but reduce long-term compliance costs for buyers.
Market expansion is particularly evident in emerging economies. India’s Plastic Waste Management Rules 2022 have created a new market for mid-range shredders, with sales jumping 40% in the past year. Brazil’s National Solid Waste Policy has similarly boosted demand for agricultural waste shredders, used to process crop residues into biofuel feedstock. These markets prioritize affordability but increasingly require basic environmental certifications, creating opportunities for cost-effective, compliant models.
For foreign trade businesses, aligning products with regional environmental policies is critical. Highlighting compliance with EU standards appeals to European buyers, while emphasizing e-waste processing capabilities strengthens positioning in North America. In Asia, promoting MSW and plastic recycling solutions can tap into growing demand. The ideal product portfolio balances advanced features for developed markets with cost-optimized, certified models for emerging economies, ensuring readiness to adapt as policies evolve globally.