With the rapid development of the electronics industry, the generation of electronic waste (e-waste) is increasing at an alarming rate. It is estimated that the global e-waste will exceed 74 million tons by 2030, posing severe challenges to environmental protection and resource utilization. In this context, shredders have emerged as indispensable equipment in the e-waste recycling process, playing a vital role in efficient and environmentally friendly disposal.
Shredders contribute significantly to e-waste recycling by breaking down bulky and complex electronic devices into smaller fragments. This size reduction not only facilitates the subsequent separation and sorting of various components but also helps in reducing the volume of e-waste, making transportation and storage more cost-effective. Moreover, shredding can effectively destroy sensitive data stored in electronic devices, preventing information leakage and ensuring data security.
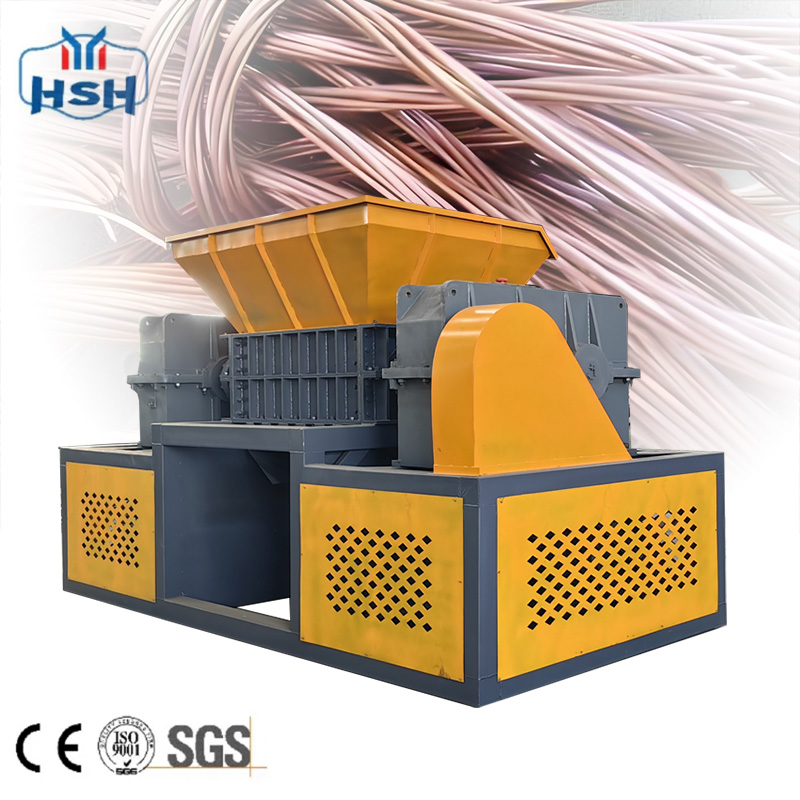

In practical applications, shredders used for e-waste recycling are often equipped with special blades and screens to handle different types of electronic components, such as circuit boards, batteries, and plastic casings. For example, when processing circuit boards, shredders can break them into small pieces, allowing for the efficient extraction of valuable metals like gold, silver, and copper through subsequent chemical or physical methods. For batteries, proper shredding under controlled conditions can prevent short circuits and hazardous substance leakage, ensuring safe recycling.
The use of shredders in e-waste recycling also aligns with the concept of a circular economy. By enabling the recovery of valuable materials from e-waste, shredders help reduce the demand for virgin resources, minimize environmental pollution, and promote sustainable development. However, it should be noted that e-waste contains various toxic substances, so shredders used in this field need to be equipped with appropriate dust removal and gas purification systems to avoid secondary pollution.
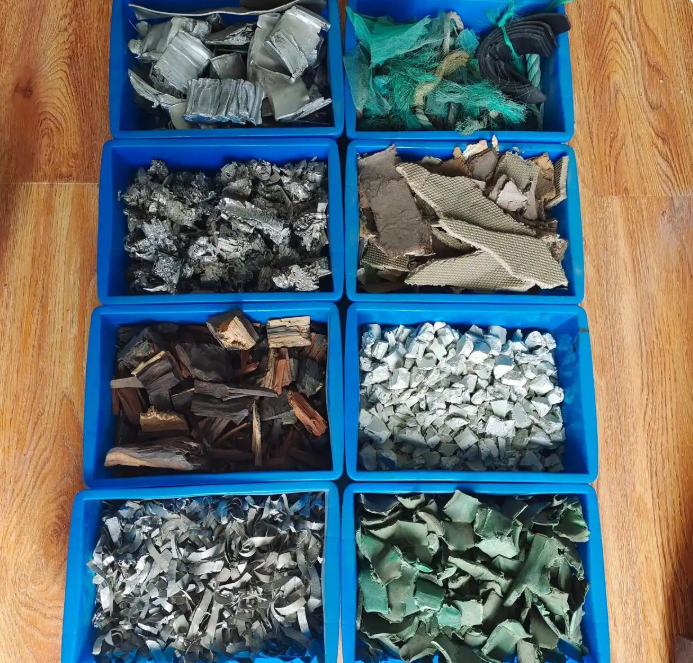

Looking forward, as e-waste recycling gains more attention worldwide, the demand for specialized shredders will continue to grow. Manufacturers are expected to develop more advanced shredding technologies that can handle a wider range of e-waste materials with higher efficiency and lower energy consumption. This will further enhance the role of shredders in promoting the sustainable management of e-waste.