As the world grapples with the escalating plastic waste crisis, shredders have emerged as indispensable equipment in the global recycling ecosystem, playing a critical role in transforming discarded plastics into reusable resources. The exponential growth in plastic consumption—from packaging materials to industrial components—has created an urgent need for efficient recycling processes, and shredders stand at the forefront of this transformation by addressing one of the most significant challenges in plastic recycling: size reduction.
Modern shredders are engineered to handle a wide range of plastic types, including PET bottles, HDPE containers, PVC pipes, and even large plastic sheets or industrial scrap. By breaking down these materials into uniform flakes or pellets, shredders not only facilitate easier transportation and storage but also prepare the plastic for subsequent processing steps such as washing, melting, and pelletizing. This size reduction is crucial because it ensures consistent material quality, which directly impacts the performance of recycled plastics in new products, from textiles to construction materials.
In addition to improving processing efficiency, shredders contribute to sustainability by reducing the energy consumption of recycling operations. When plastics are shredded into smaller pieces, they require less heat and energy during melting compared to larger chunks, lowering the carbon footprint of the recycling process. Furthermore, advanced shredder designs with features like variable speed controls and energy-efficient motors have further enhanced this eco-friendly aspect, aligning with global efforts to achieve carbon neutrality.
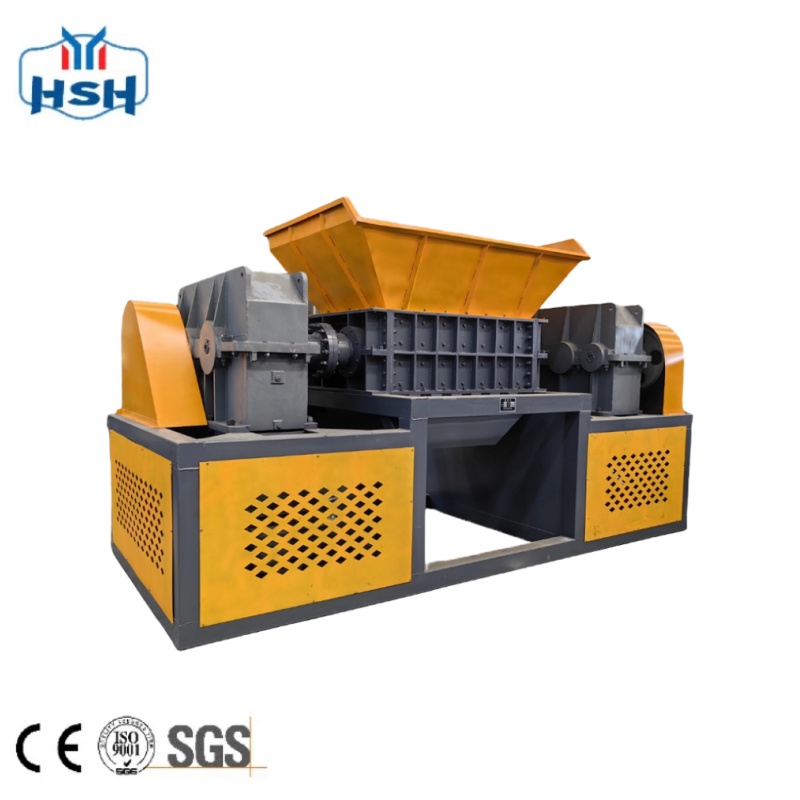

The adoption of shredders in plastic recycling has also been accelerated by evolving regulations aimed at curbing plastic pollution. Governments worldwide are implementing stricter waste management laws, such as extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes, which require manufacturers to take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of their plastic products, including recycling. This has led to increased investments in recycling infrastructure, with shredders being a key component of new recycling facilities, both in developed and emerging economies.
Regionally, the demand for plastic recycling shredders varies based on local recycling capacities and policy support. In Europe, where plastic recycling targets are among the strictest globally, shredder adoption is high, with many facilities utilizing high-capacity industrial shredders to meet ambitious recycling rates. In Asia, rapid urbanization and growing awareness of plastic pollution have driven significant investments in recycling technology, making the region a fast-growing market for plastic shredders. Meanwhile, North America is seeing increased adoption of specialized shredders designed for post-consumer plastic waste, supported by both government funding and private sector initiatives.

Looking ahead, the role of shredders in plastic recycling is set to become even more critical as the world moves toward a circular economy for plastics. Innovations in shredder technology, such as the integration of artificial intelligence to optimize shredding processes and sensors to monitor material flow, are expected to further improve efficiency and reduce operational costs. Additionally, the development of shredders capable of handling mixed plastic waste—long a challenge in recycling—could unlock new opportunities for increasing recycling rates and reducing plastic waste sent to landfills or incineration.
In conclusion, shredders are not just pieces of machinery but essential enablers of a more sustainable approach to plastic waste management. Their ability to efficiently process diverse plastic materials, reduce energy consumption, and support compliance with environmental regulations makes them a cornerstone of global efforts to tackle plastic pollution. As recycling technologies continue to advance, shredders will remain a key investment for businesses and governments committed to building a circular economy for plastics.