Shredder: The “strongman” of green recycling
In recent years, environmental protection and sustainable development have become global consensus, with resource recycling and waste disposal emerging as critical issues. Shredders, as highly efficient crushing equipment, are increasingly demonstrating their unique value across various industries.
As the name suggests, shredders are primarily used to shred various materials. Whether it's raw materials, scrap materials, or discarded items, shredders can utilize their powerful crushing capabilities to break them down into smaller fragments, facilitating subsequent processing, treatment, or reuse.
Firstly, shredders play a significant role in the recycling of plastic waste. The massive production of plastic waste has become one of the primary sources of environmental pollution. Through shredder processing, plastic waste can be broken down into smaller particles, facilitating subsequent recycling. These particles, after further processing, can be used to manufacture new plastic products, achieving the circular utilization of resources.

Secondly, shredders also play a key role in the recycling of scrap metal. Metal resources are limited, and the recycling and reuse of scrap metal can effectively reduce the extraction of virgin resources. Shredders can break down scrap metal into small pieces, making it easier for subsequent sorting and smelting. In this way, scrap metal is given new life, providing a steady supply of raw materials for industrial production.
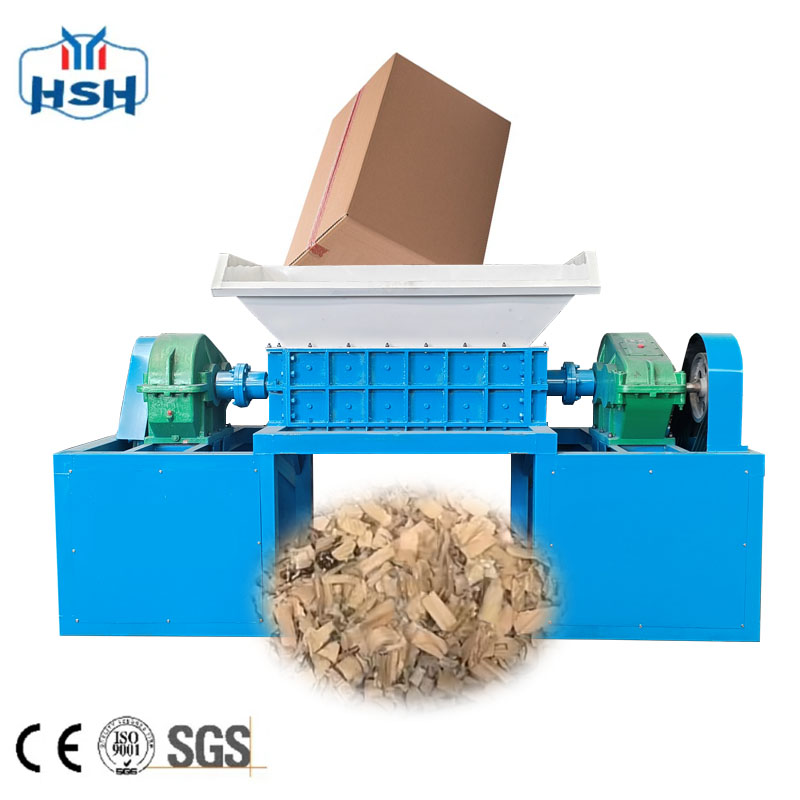
Additionally, shredders have widespread applications in the recycling of scrap wood, electronic waste, and other materials. For scrap wood, shredders can break it down into wood chips or sawdust, which can be used to produce biomass energy or as raw materials for the paper, plywood, and other industries. For electronic waste, shredders can break it down into smaller components, facilitating the subsequent separation and recovery of precious metals and useful materials.
Beyond these fields, shredders play a crucial role in numerous other industries. For example, in the processing of fruit and vegetable waste, shredders can break down the waste into smaller pieces, facilitating subsequent fermentation and composting processes. In the handling of bulky waste, shredders can reduce large items into smaller fragments, minimizing the space they occupy and lowering processing costs.
The working principle of shredders primarily relies on their internal cutting blades or gears. Materials enter through the shredder's inlet, undergo shearing, tearing, and crushing by rotating cutting blades or gears, and are then discharged from the outlet as smaller fragments. This crushing method is not only highly efficient but also produces uniform results, meeting the needs of various industries.
In summary, shredders, as highly efficient crushing equipment, play a significant role in multiple fields. They not only facilitate resource recycling and reduce waste generation but also contribute to environmental protection and sustainable development. With ongoing technological advancements and expanding application areas, the role of shredders will become increasingly prominent, providing strong support for building a green and circular society.